 Here's some news that should surprise nobody. International efforts to suppress the trade in a psychoactive plant are failing to do so, but are jacking up the social costs of its use—which might be quite negligible if the stuff weren't illegal. In this case we're talking about khat, the mildly stimulating leaf that is chewed socially in the Horn of Africa and its immigrant diaspora. It was sold openly at groceries and eateries in London's African communities until Britain finally banned the stuff in of 2014, following the example of the United States (of course). At that time, it became a Class C substance under the UK Misuse of Drugs Act. By way of comparison, cannabis is in the more restrictive Class B—although between 2004 and 2008 pot was placed in Class C, and there is an initiative to have it removed from the classification system altogether.
Here's some news that should surprise nobody. International efforts to suppress the trade in a psychoactive plant are failing to do so, but are jacking up the social costs of its use—which might be quite negligible if the stuff weren't illegal. In this case we're talking about khat, the mildly stimulating leaf that is chewed socially in the Horn of Africa and its immigrant diaspora. It was sold openly at groceries and eateries in London's African communities until Britain finally banned the stuff in of 2014, following the example of the United States (of course). At that time, it became a Class C substance under the UK Misuse of Drugs Act. By way of comparison, cannabis is in the more restrictive Class B—although between 2004 and 2008 pot was placed in Class C, and there is an initiative to have it removed from the classification system altogether.

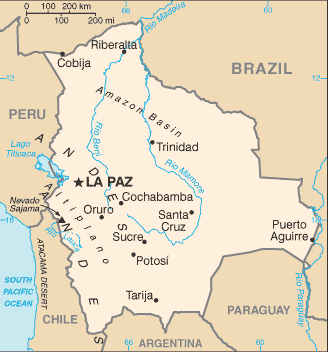 Among the coca-growing peasants of Bolivia's Yungas region (the country's prime legal cultivation zone) is a substantial Afro-Bolivian population—descendants of slaves who were brought in by the Spanish colonialists to work in the silver mines and haciendas centuries ago. Some have inter-married with the indigenous Aymara people of the Yungas, forming a distinctive Afro-Aymara culture.
Among the coca-growing peasants of Bolivia's Yungas region (the country's prime legal cultivation zone) is a substantial Afro-Bolivian population—descendants of slaves who were brought in by the Spanish colonialists to work in the silver mines and haciendas centuries ago. Some have inter-married with the indigenous Aymara people of the Yungas, forming a distinctive Afro-Aymara culture.  Sudan's conflicted western region of Darfur has receded from the headlines since the wave of
Sudan's conflicted western region of Darfur has receded from the headlines since the wave of 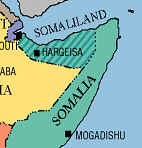 Here's a telling irony. We think of Somalia as a country that has basically had no functioning government for over a generation, and is beset by insurgents linked to al-Qaeda. Certainly, how a government treats a relatively harmless psychoactive herb is a good barometer of its general commitment to freedom. The herb in question here is khat, the mildly stimulating leaf that is chewed socially throughout the Horn of Africa. And
Here's a telling irony. We think of Somalia as a country that has basically had no functioning government for over a generation, and is beset by insurgents linked to al-Qaeda. Certainly, how a government treats a relatively harmless psychoactive herb is a good barometer of its general commitment to freedom. The herb in question here is khat, the mildly stimulating leaf that is chewed socially throughout the Horn of Africa. And  The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (





Recent comments
6 weeks 2 days ago
6 weeks 2 days ago
9 weeks 3 days ago
10 weeks 2 days ago
14 weeks 2 days ago
18 weeks 1 day ago
22 weeks 1 day ago
22 weeks 6 days ago
32 weeks 6 days ago
37 weeks 5 hours ago